KYOCERA SGS Precision Tools, Inc., formerly known as the SGS Tool Company and a wholly-owned subsidiary of KYOCERA Corporation, was originally founded in 1951 and is an ISO-certified leader of round solid carbide cutting tool technology for the aerospace, metalworking, and automotive industries. Today, it is best known for its solid carbide high performance end mills and drills. However, it is also well known for its stainless steel medical tools and technically advanced, proprietary PVD coatings. KYOCERA SGS Precision Tools, with manufacturing sites in the United States and United Kingdom, aggressively services its customers through a global network of Sales Representatives, Industrial Distributors, and Agents that sell into more than 60 countries.
In the realm of CNC machining, tool wear and damage are perpetual challenges that can significantly impact productivity and tool longevity. The primary factors influencing these issues are speed and feed. This article delves into these concepts, providing CNC machinists with a detailed exploration of how to balance these parameters for optimal performance.
Fundamentals of Speed and Feed
Speed and feed are fundamental to the machining process. Speed, or revolutions per minute (RPM), refers to the rotational speed of the tool or the workpiece. Feed, on the other hand, is the rate at which the tool advances into the material. Synchronizing these two parameters is crucial; an imbalance can lead to rapid tool wear and suboptimal machining results.
Watch now to optimize your speeds and feeds: Is Speed and Feed Killing Your Tooling?
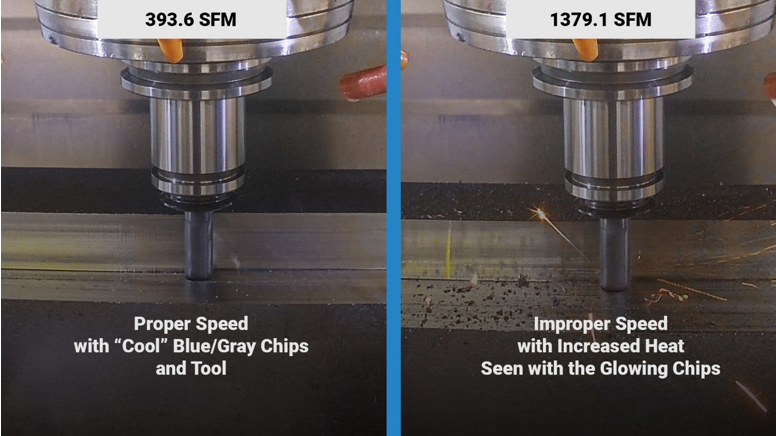
It’s important to note that RPM is a resultant value influenced by both the surface speed (or cutting speed, SFM) and the cutter diameter. Surface speed is a more precise and practical metric for CNC machining as it directly relates to the tool’s interaction with the material. Focusing on surface speed can provide a more consistent basis for optimizing machining parameters.
Achieving the Optimal Balance
The key to maximizing both productivity and tool life lies in finding the “sweet spot” between speed and feed. While manufacturers provide speed and feed charts as a baseline, these are conservative estimates that often do not account for the numerous variables present in real-world machining environments.
“It’s not about taking your speeds and feeds to the maximum or bringing them all the way down to the minimum. It’s about trying to find that sweet spot that allows you to maximize your productivity and your tool life,” says Jason from Kyocera SGS, who works in Research and Development.
As machinists, we know that pushing beyond the provided parameters can sometimes yield better productivity, but it’s a balancing act. We have to tread carefully, adjusting parameters based on real-world results to avoid adverse effects. This delicate balance between caution and efficiency is what makes our work both challenging and rewarding.
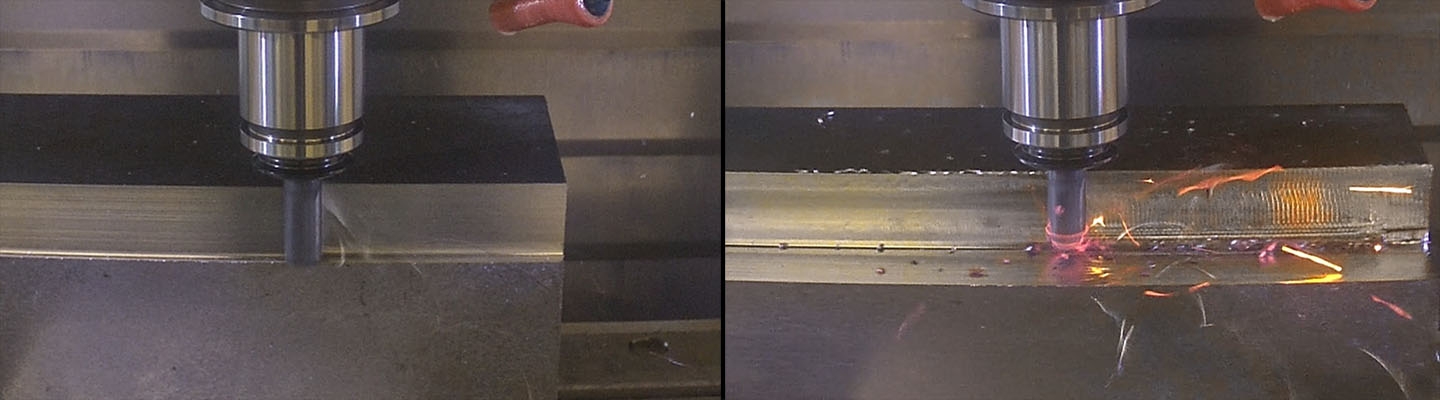
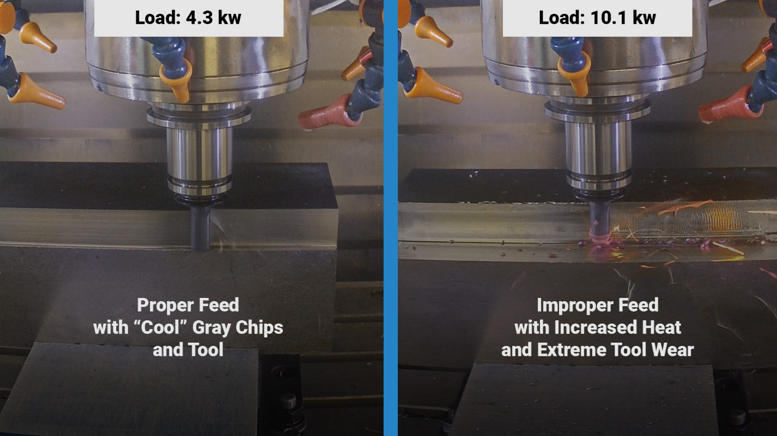
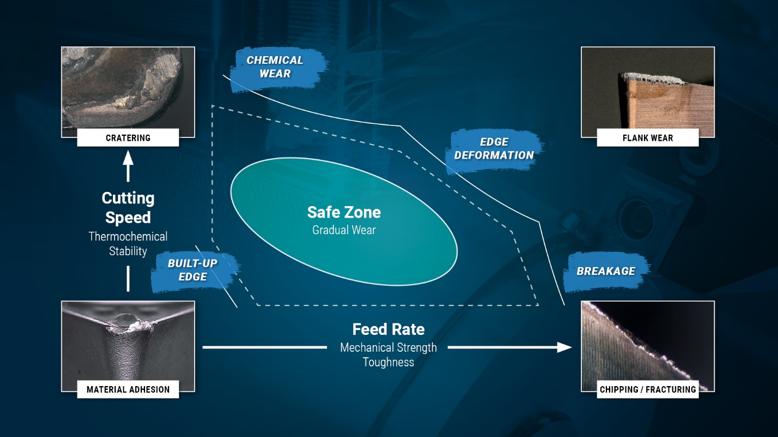
Diagnosing Tool Wear: Heat and Load
Major Sources of Tool Wear
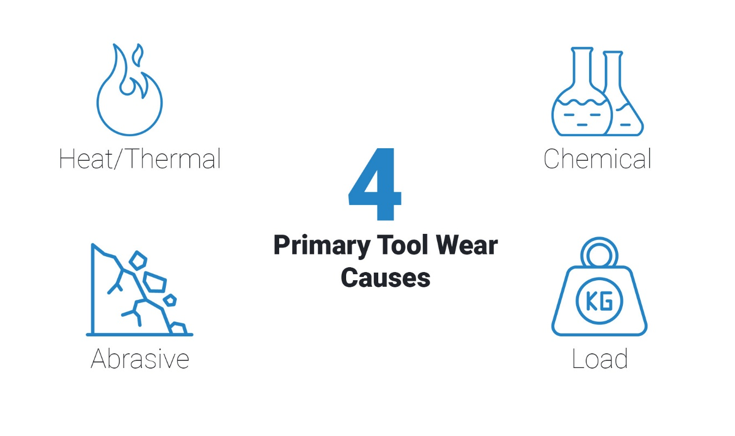
Tool wear can be attributed to four primary sources: thermal, abrasive, chemical, and load. For simplicity, we can narrow these down to two main categories: heat and load. Understanding these categories is essential for diagnosing and addressing tool wear effectively.








Talk to Us!
Leave a reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *