Caliper Calibration: What Is Measurement Uncertainty?
This technical bulletin provides an example evaluation of measurement uncertainty for the calibration of a 0-150 mm digital caliper such as a 500 series caliper from Mitutoyo.
This technical bulletin provides an example evaluation of measurement uncertainty for the calibration of a 0-150 mm digital caliper such as a 500 series caliper from Mitutoyo.
This technical bulletin provides an example evaluation of measurement uncertainty for the calibration of a 0-150 mm digital caliper such as a 500 series caliper from Mitutoyo. In the American national standard on calipers, ASME B89.1.14-2018, and the international standard for calipers, ISO 13385-1:2019, there are general rules and guidance on the evaluation of measurement uncertainty, and the example in this technical bulletin follows those standards. In addition, the evaluation of measurement uncertainty in this technical bulletin is in accordance with the GUM, the Guide to the Expression of Uncertainty in Measurement (JCGM 100:2008 or ISO/IEC Guide 98-3:2008), as well as ILAC-P14:09/2020, which has important measurement uncertainty policies for calibration laboratories accredited to ISO/IEC 17025:2017.
In this example, the purpose of the measurement is to assess conformity of the caliper to the specified maximum permissible error (MPE) called the partial surface contact error. This specification is defined in ASME B89.1.14 and ISO 13385-1 and is denoted EMPE. This length measurement error is typically assessed in calibration using some type of length standard, such as gage blocks. For this example, the manufacturer’s specification is assumed to be EMPE = ± 20 µm at a length of 150 mm. This measurement uncertainty example was taken directly from Appendix C of ASME B89.1.14.

Important assumptions and conditions:
Reference standard (Grade 0 gauge block) has a specification of ± 0.40 µm and is assumed to be within tolerance.
Environmental conditions during calibration: 20 ± 2°C.
Caliper coefficient of thermal expansion (CTE): 11.5 x 10-6/°C ± 10% (therefore ± 1.15 x 10-6/°C).
Gauge block coefficient of thermal expansion (CTE): 10.2 x 10-6/°C ± 5% (therefore ± 0.51 x 10-6/°C).
The difference in the CTE is therefore 1.3 x 10-6/°C, and the average CTE is 10.85 x 10-6/°C.
Temperature difference between caliper and gauge blocks is assumed to be within ± 0.5 °C.
The values above were taken directly from the worked measurement uncertainty example in ASME B89.1.14 and are used for example purposes only. Further details on the calculations can be found in that standard. The uncertainty contributors and necessary calculations are summarized in the table below. In accordance with ASME B89.1.14, this example is complete and no further measurement uncertainty contributors are necessary. Mitutoyo America follows this approach for the accredited calibration of calipers with the only difference being the addition of the calibration uncertainty of the reference standard.
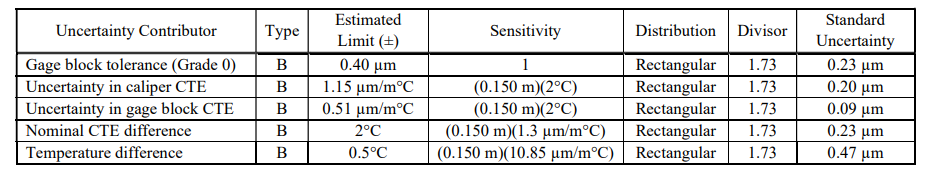
• The combined standard uncertainty is calculated as: uc = (0.232 + 0.202 + 0.092 + 0.232 + 0.47)½ = 0.61 μm • The expanded uncertainty, using k = 2, is calculated as: U = 2uc = ± 1.2 μm
The calibration information needed by the owner or user of a caliper is that the caliper conforms to specifications. In ASME B89.1.14 and ISO 13385-1, the default decision rule is simple 4:1 acceptance. In accordance with this decision rule, an assessment of conformity requires the measurement uncertainty to be 25% of the tolerance or less. In this case, the uncertainty of ± 1.2 μm is only 6% of the ± 20 μm tolerance, and therefore conformity can be assessed.
The evaluation of measurement uncertainty must always consider how the instrument being calibrated contributes to the measurement uncertainty. In this example, this can be seen where the uncertainty associated with the material of the caliper, and the influence of temperature, is included in the measurement uncertainty evaluation. In the calibration of a caliper, the intention is to measure the errors of the caliper and assess conformity. The measurement errors of the caliper due to inherent design limitations and imperfections, e.g. caliper repeatability, resolution, and mechanical errors, contribute to the measured values but not the measurement uncertainty. The purpose of the caliper calibration is to assess measurement error, and the uncertainty is a measure of the quality of those values but not a measure of the quality of the caliper itself. When the intention of the calibration is to measure the errors and assess conformity, then including measurement errors of the instrument being calibrated as contributors to the measurement uncertainty of the calibration is inappropriate and not in accordance with American and International dimensional metrology standards.
In accordance with ASME B89.1.14 and ISO 13385-1, the user of a caliper must be reasonably skilled to properly assess conformity with specifications. As such, the specifications of a caliper include the influence of a reasonably skilled operator, and this influence is therefore included in the assessment of the caliper during calibration and not also estimated and included as a contributor to the measurement uncertainty. Mitutoyo America offers training, proficiency testing, and certification of operator skill in the calibration of calipers.
The measurement uncertainty in the calibration of dimensional measuring instruments is addressed in the general uncertainty standards ISO 14253-5:2015 and ASME B89.7.6-2019. The relationship between verification testing and calibration is addressed in the standards ISO 14978:2018 and ASME B89.7.1-2016. Mitutoyo America also offers a book and eLearning training class to assist in disseminating this critical information.
Previously Featured on Mitutoyo's Resource Center.
Browse Mitutoyo calipers on MSCDirect.com.
Established in 1963, Mitutoyo offers a full product line of precision measuring tools including calipers, micrometers and indicators, as well as instruments and equipment. Mitutoyo is the leading metrology company in the world and is committed to developing breakthrough technologies for its comprehensive range of dimensional measuring tools, instruments and systems. Mitutoyo continues to develop the most advanced and sophisticated metrology equipment available.
