OSHA and Safety Glasses
Eye injuries alone cost companies more than $300 million per year in lost production time, medical expenses, and worker compensation.
Eye injuries alone cost companies more than $300 million per year in lost production time, medical expenses, and worker compensation.
After worksite inspections were completed by the Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA) in 2018, they found that one of the top 10 most frequently cited violations is 29 CFR 1926.102—the eye and face personal protection safety and health regulation for the construction industry. And, if there is one industry where workers need to be wearing safety glasses, it is the construction industry. According to the Bureau of Labor Statistics (BLS), in 2019 the construction industry had the second-highest eye injury rate, accounting for over 13% of all on-the-job injuries.
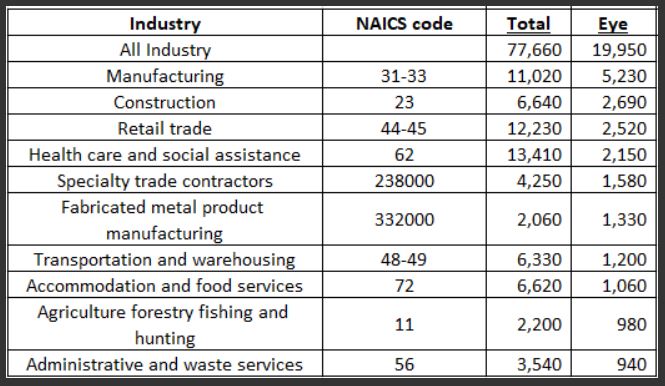
Not only that, but eye injuries alone cost companies more than $300 million per year in lost production time, medical expenses, and worker compensation.
Read more: 2020 OSHA Top 10 Violations: What They Cost and Tips to Avoid Them
OSHA and the BLS publish this information to alert employers of potential concerns and dangers present. This data allows employers to take steps to find and fix the hazards that can cause citations in the first place. Even more so, it helps prevent people from getting hurt. Unfortunately, many risks, such as exposure to heat, dust, and chemicals, are characteristics of the jobs people perform.
As a result of these potential hazards, OSHA requires employers to provide eye and face protection for all employees. Both employers and workers need to be responsible for the prevention of thousands of work-related eye injuries by staying informed about the proper selection and use of eye and face protection. Below, MCR Safety highlights all you need to know about safety glasses and eye protection.

OSHA breaks down applicable standards into several categories that ensure workers are protected in the workplace. Here is a quick snapshot of each one:
General requirements: 29 CFR 1910.132 – requires employers to provide, at no cost to employees, appropriate PPE, including safety glasses, for protecting the body from hazards.
General industry: 29 CFR 1910.133 – employers shall guarantee that each affected employee uses proper eye or face protection when subjected to eye or face hazards from:
flying particles;
molten metal;
liquid chemicals, acids, or caustic liquids;
chemical gases or vapors, or potentially injurious light radiation.
Construction industry: 29 CFR 1926.102 – specific regulations are set for construction-based environments. As MCR Safety highlighted above, the construction industry involves dangerous activities, reflected in the number of eye injuries.
All eye and face PPE must meet minimum requirements to provide adequate protection, such as durability, easy cleaning and disinfecting, a snug, comfortable fit, and safe, effective design and construction. Also, all PPE must be distinctly marked to facilitate identification only of the manufacturer.

MCR highlighted OSHA's regulations above. Now, they cover some additional requirements outlined by OSHA. The Eye and Face Protection eTool is a web-based training tool that provides compliance information to help employers and workers in selecting the proper eye and face protective equipment as it applies to the potential eye and face hazards in different working conditions.
29 CFR 1910.132(d) says an employer must first assess the workplace for hazards that require eye and face protection. 29 CFR 1910 Subpart I App B explains that the hazard assessment should determine the risk of exposure to eye and face dangers during normal operations and emergencies. Employers should be prepared to protect workers against the highest level of each hazard.
Check out the frequently asked questions on OSHA's eye and face protection eTool page for more information.
The four main hazards most likely to cause eye injury if workers are not appropriately protected are heat, chemicals, dust, and impact. MCR Safety highlights all four below, along with welding eye hazards, too.
Serious and irreversible damage can occur when chemical substances make direct contact with the eyes in the form of splash, mists, vapors, or fumes. Many times, injuries happen when handling acids and chemicals, degreasing, and plating.
When working with or around chemicals, you must know the location of emergency eyewash stations and how to access them with restricted vision.
OSHA PPE guidance for chemical hazards:
Chemical eye injuries often result from an ill-fitting or inappropriate choice of PPE, allowing a chemical substance to enter from around or under the protective eye equipment.
Safety goggles shield the eyes from liquid or chemical splash, irritating mists, vapors, and fumes, while face shields protect the entire face against exposure to chemical hazards.
Working in a dusty environment such as buffing, woodworking, or construction sites can cause eye injuries and present additional hazards to contact lens wearers. Safety goggles and lined safety glasses are the only useful type of eye protection from nuisance dust because they create a protective seal around the eyes.
OSHA PPE guidance for dust hazards:
Safety goggles protect the eyes against a variety of airborne particles and harmful dust.
Burns to eyes and facial tissue is the primary concern when working with heat hazards. Heat injuries may occur when workers are exposed to high temperatures, splashes of molten metal, or hot sparks. A worker must protect their eyes from numerous workplace operations that involve heat: pouring, casting, hot dipping, furnace operations, and other similar activities.
Working with heat hazards requires eye protection such as goggles or safety spectacles with special-purpose lenses and side shields. However, many heat hazard exposures require the use of a face shield in addition to safety spectacles or goggles. When selecting personal protective equipment, consider the source and intensity of the heat and the type of splashes that may occur in the workplace.
OSHA PPE guidance for heat hazards:
Safety glasses and safety goggles shield the eyes from a variety of heat hazards, while face shields protect the entire face from many heat hazards.
Serious eye injuries such as punctures, abrasions, and contusions can result from flying objects like large chips, fragments, particles, sparks, sand, and dirt, or falling objects (which can be smaller than a pinhead) striking the eye.
Many everyday workplaces can create this type of hazardous environment with routine activities. Here are some: chipping, grinding, machining, masonry work, woodworking, sawing, drilling, chiseling, powered fastening, riveting, and sanding. The injuries sustained from an airborne particle hitting one's eye can be permanent, which means wearing safety glasses is an absolute must.
OSHA PPE guidance for impact hazards:
Safety glasses shield the eyes from a variety of impact hazards. Safety goggles shield the eyes against flying fragments, objects, large chips, and particles. Face shields protect the entire face against exposure to impact hazards.
Welding, cutting, soldering, and brazing protection are especially important. The intensity of visible light and radiant energy produced by welding operations vary depending on the task, the electrode size, and the arc current. Eyes must be protected from burns caused by infrared or other intense radiant energy from flying sparks, metal spatter, and slag chips.
Only filter lenses with the appropriate shade number will protect against optical radiation. Filter lenses must coincide with specific radiant energy exposure. Welding helmets shield the eyes and face from optical radiation, heat, and impact.
OSHA PPE recommendations for welding and cutting hazards:
MCR Safety highlights all their cutting glasses and welding filter shaded glasses on their Welding Protection page. You will also find some brand-new welding glove options when you're there, too.
Previously Featured on MCR Safety's blog.
MCR Safety has over forty years of experience as a leader in the field of personal protective equipment (PPE).Our assortment of offerings includes gloves, glasses, and garments which are made from the highest quality materials available to ensure maximum safety, comfort, and style. Products formally promoted under our legacy brands, such as, Memphis Gloves, Crews Glasses, and River City Garments; are being transitioned to our full line branding of MCR Safety.
